Where Is Fear Registered In The Brain?
Abstract
If you encountered a bear in the forest what would you do? In this article, we volition talk about what stress is and how our brains and bodies react to information technology. There are many cool things that happen within of the human body when nosotros are faced with a scary situation. We volition focus on the brain regions that are responsible for our reactions to stress. Nosotros will learn how they help our bodies to at-home downwards when faced with something scary. The main parts of the brain that are responsible for our reactions to stress include the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, the amygdala, and the prefrontal cortex. This article will also embrace how the brain gets help from outside sources and how humans adapt to stress when it becomes a normal part of life. Let us read all about the superheroes that aid us to overcome fifty-fifty the scariest situations!
What is the Stress Response Organization?
Imagine how you lot would feel if yous encountered a bear in the woods. Your heart might start racing and you might start breathing heavily. You might freeze in place, unable to move out of fear. You might feel the urge to run away. These are all symptoms of stress . Stress is the mental and physical state humans feel when they experience something hard or threatening. Stress can come from many different sources. Normal stressors are things that make you experience nervous or scared for a short fourth dimension, like talking in front of a large group of people. Bigger, long-lasting stressors make you experience pitiful or scared for a long fourth dimension. The death of a close family unit fellow member is one instance. The good news is that your encephalon is a superhero! Every day it keeps you safety from too much stress.
The brain gets help from other organs to calm you lot down when you face scary or pitiful stressful situations. The stress–response system is the proper name of the squad of superheroes in your torso that is led by the encephalon to gainsay stress. The stress–response system takes action by speeding upward your centre beat to increase claret menstruation, speeding up your breathing to take in more oxygen, and slowing your digestion to store away fatty and saccharide for energy. In this commodity, nosotros will talk most how the brain and body react to stress and how the brain regulates these reactions. We will also talk about the outside help the brain uses to regulate stress considering even superheroes need a niggling help sometimes! Finally, we will larn how humans adapt to stress when it is long lasting.
Superheroes of the Stress Response System
When the brain detects stress in the environs, the stress–response arrangement goes into action. This begins with the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis (Figure 1). Those are some very long words, so scientists only call it the HPA axis. When the brain detects stress, it first sends a bulletin to a function of the brain called the hypothalamus. The job of the hypothalamus is to wake upward the pituitary gland. Although the pituitary is only about the size of a small pea, it has a mighty job. The pituitary releases hormones, which are the messengers in the stress–response system. These hormones travel out of the encephalon to the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands sit on peak of the kidneys. The adrenal glands release cortisol into the body.
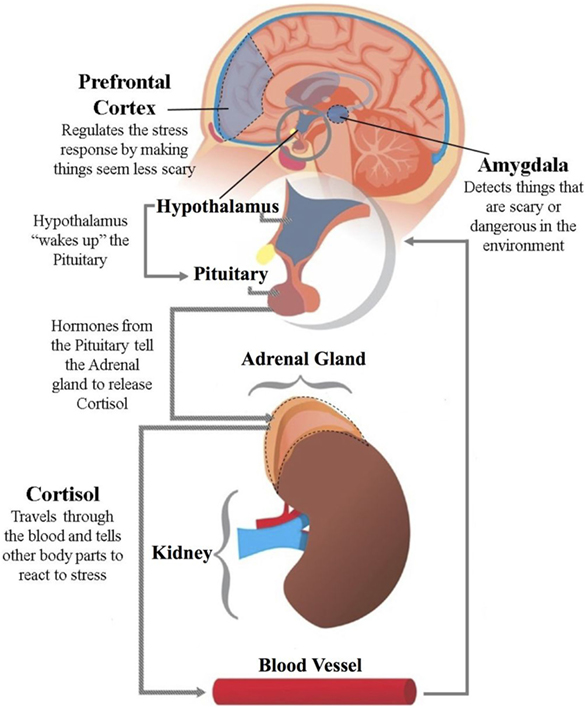
- Figure one
- The hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis acts to release cortisol into the blood stream. Cortisol calls the trunk into activeness to gainsay stress. Cortisol too regulates the HPA axis. When high amounts of cortisol interact with the hypothalamus, the HPA axis will dull downward its activeness. The amygdala detects stress in the environment, while the prefrontal cortex regulates our reactions to stress.
Cortisol is known as the stress hormone. Cortisol is a messenger that sets other organs in the body into action. Information technology is like the superpower of the stress response system. Cortisol helps the brain to think clearly, sends free energy to important muscles, and increases heart rate and breathing. You tin imagine that all of these bodily functions would be important if you were face-to-face with a bear: you lot would need to call up about how to escape, utilise your muscles to run away, and have a fast heartbeat to pump lots of blood to the muscles and fast breathing to take in more oxygen [1].
Another of import brain construction involved in the stress response organization is called the amygdala . This funny-sounding encephalon structure is the size of a small kidney bean. It is located in the middle of the brain (Effigy 1). The amygdala is the brain structure that actually detects stress and tells the HPA centrality to respond. It can notice both emotional and biological stressors. An emotional stressor is something in the surroundings that may cause you to feel scared, sad, or frustrated, like the bear. A biological stressor is internal stress felt by the body, considering of an injury or illness [1]. These functions of the amygdala are extremely important for survival. Simply recall—if you could not find things that are harmful or stressful, you would not survive!
The amygdala shares a special connection with some other part of the brain called the prefrontal cortex . The prefrontal cortex is a big region in the front of the brain (Figure 1). Information technology can exist called the command center of our brains considering it helps to control our thoughts and actions. The main chore of the prefrontal cortex is to control our emotional responses to stress so that we practice non get too stressed out. This is why the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex share a special connection [ii]. The amygdala rapidly signals a threat or stress in the surround, and the prefrontal cortex helps the amygdala to run into stressful events as a little less scary or frustrating. Information technology is important to be able to use the brain to aid ho-hum the production of cortisol in the HPA axis. This procedure helps the states calm down during a normal stressor by perceiving the situation every bit non-life threatening. In the behave example, which is a real danger, this process would aid united states to at-home down after the comport runs abroad.
Fifty-fifty Superheros Sometimes Demand Assistance
Even though our bodies accept these super stress–response systems, humans are best at dealing with stress when they have a fiddling help. This assist is chosen social back up, which refers to the ways that other people can aid us experience safe, loved, and cared for [i]. Your friends and family may provide social back up by hugging y'all when yous are sad or scared, hanging out with you when y'all feel lonely, or celebrating with you when you are excited. We particularly need social support when we are very young. Remember earlier when we mentioned that the amygdala shares a special connectedness with the prefrontal cortex? This connexion does non mature until you are a teenager; therefore, infants and children rely on their parents to assist them calm down.
Scientists have studied how the brain responds to stress using a special technique called functional magnetic resonance imaging, or fMRI for curt. fMRI is like a big camera that takes pictures of our insides using magnets. fMRI can assist scientists detect which areas of the encephalon are active during certain tasks. Scientists did an experiment to find out how moms help their children deal with stress. Children (ages 4–10) and teenagers (ages 11–17) viewed emotional faces on a figurer screen. Some of the faces showed negative emotions, like sadness or fearfulness. Considering seeing these negative emotional faces could exist stressful, the amygdalas of the children and teenagers became agile when these faces were viewed [2]. Children who had their mothers next to them every bit they viewed the faces showed lower amygdala activity (Figure ii). These children besides had more mature connections between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex when their mothers were nearby! This means that the children' prefrontal cortex was activating more than and their amygdala was activating less, helping the children experience less stressed. When people, like the moms in this experiment, provide social support that helps regulate the stress response, it is called social buffering . Buffering means to protect or shield. In the experiment, we just talked most, the children's moms were buffering, or protecting the amygdala from too much activity. Social buffering that comes from mothers is called maternal buffering. Research has shown that moms and other caregivers (like dads and babysitters) assistance to lower the cortisol levels in babies and kids who accept experienced a stressful situation [1].
![Figure 2 - This study [2] compared the brains of children and teenagers while they viewed emotional faces.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/303001/frym-05-00071-HTML-r1/image_m/figure-2.jpg)
- Figure two - This study [two] compared the brains of children and teenagers while they viewed emotional faces.
- When looking at negative emotional faces (sad, aroused, etc.) you tin see that the children's amygdala activity was decreased when their mothers were present. This tells us that the moms were buffering stress–response systems in the children by providing social support. The teenagers' amygdala action increased when they viewed the emotional faces fifty-fifty though their mothers were present.
The results of the study are even more amazing considering the scientists did not detect maternal buffering when teenagers did the same task with their mothers next to them. Does this mean that teenagers no longer need their moms? Evidence from some other report show that teens nevertheless need their moms, but in a dissimilar fashion. In this experiment, the scientists had teenagers play a risky driving video game alone and when their moms were present. In the game, teenagers approached a yellowish light that was about to plough red. They had to decide if they should drive through the light and risk getting into a machine accident. They found that teens made more than safe choices when their moms were nowadays, and only similar the study higher up, the mom's presence helped the prefrontal cortex come into activity [3]. This study demonstrates that teens also need the support of their moms to make skillful choices!
What Happens When Stress Lasts a Long Time?
Stress comes in many unlike forms. The instance we have used throughout this commodity is encountering a behave. Seeing a bear is typically a brusque-term stressor, considering you would probably get out of that stressful situation chop-chop. Feeling stressed is normal and good for detecting danger in the surroundings. But for some people, stress becomes a normal part of life. Imagine if you were bullied at school. Going to school every 24-hour interval might get scary or stressful. Short-term stress causes curt bursts of a lot of cortisol. If the HPA axis is activated continuously, every bit with long-term stress, the stress–response system will change to try and deal with long-term stress [1]. The stress–response organisation changes by making less cortisol since there is and then much in the body. This causes an imbalance of cortisol and poor functioning of the stress–response organization.
One situation that might crusade long-term stress is very poor care early on in life, such equally living in an orphanage without parents. A study (meet Figure 3) compared children who lived in orphanages to children who grew up with their parents. Like to the final study we talked about, the scientists looked at the children's brains while they viewed emotional faces [4]. They also compared the children' brains to teenagers' brains while they viewed these faces. The scientists likewise focused on the connection betwixt the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala to study how these children regulated emotional stress. What they establish was that the orphaned children'due south brains looked more than like the teenagers' brains than the non-orphaned children. So the orphaned children's brains were actually more than mature! This means that their brains were able to regulate their emotional stress even without a parent nearby.
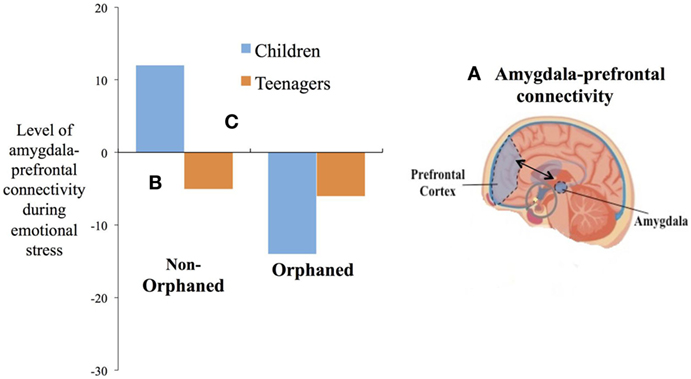
- Figure three - The brain A. shows the connection between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex.
- The graph shows how the amygdala and prefrontal cortex are connected while the children and teenagers viewed emotional faces. Bars in the negative management B. indicate that the amygdala becomes less agile considering the prefrontal cortex becomes more active. This is what happens during regulation of emotional stress. Bars in the positive direction C. indicate that both the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex are condign more active. This is what happens when the brain is not able to regulate stress. You tin can see that the bars for orphaned children and teenagers both go in the aforementioned direction (negative). The bars for the not-orphaned children and teenagers get in contrary directions [four]. This tells the states that in the absence of adept early care these areas of the brain are maturing faster.
Information technology might sound like a expert thing to accept a mature brain. But this is not always true for humans. Humans take a long fourth dimension to mature. The normal pattern of homo development allows humans to learn a lot nigh how to be an developed before really condign one. The children in this study lived in very crowded orphanages without much love and affection from adults. Without a close human relationship with an adult as young children, the orphaned children'south brains had to become mature much sooner. Becoming mature too soon is related to more feet, a mental state of worry and fear [four]. The good news is that children who are adopted eventually feel social buffering from stress when they feel loved and supported by their adopted family unit [one].
Determination
The encephalon fights stress every unmarried day. Whether an enormous behave is chasing you or you see a small spider in your room, the brain and the body are ready and equipped to deal with the stress. Our brains are like superheroes—prepare to relieve the day! With the help of the HPA centrality, the amygdala, and the prefrontal cortex, nosotros can at-home ourselves down during stressful situations. No one can become through everything alone, not even superheroes. Our brains sometimes rely on the help of our friends and families to help buffer the response to stress. Parents are extremely helpful, especially when nosotros are young. In the absence of a caregiver at a immature age, a child'south encephalon may become mature too fast, which may brand a kid feel anxiety. Anxiety makes things seem scarier than they actually are, which will make the child feel even more stressed! At that place are things you can do to handle short-term and long-term stress in your own life. Doing any activity that you bask releases chemicals in your brain that make yous feel happy. Exercising and moving your body are bully ways to reduce stress. Another way to handle stress is spending time with friends and family. Remember that having people in your life who provide social support can make y'all feel cared for, which volition ho-hum the release of cortisol. The best thing to do is tell a trusted adult if you are feeling stressed for a long period of time!
Glossary
Stress: ↑ The mental and physical land humans feel when they experience something difficult or threatening.
Stress Response Organization: ↑ The name for the parts of the encephalon, organs, and hormones that piece of work together to combat stress.
Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) Axis: ↑ The messenger system that begins in the brain. It signals the organs to react to stress past going into survival mode. It includes the hypothalamus, the pituitary, and the adrenal gland.
Cortisol: ↑ The stress hormone, or messenger, that is released by the HPA axis to tell other organs in the body to bargain with a stressor.
Amygdala: ↑ The brain structure that actually detects stress and tells the HPA axis to respond.
Prefrontal Cortex: ↑ The control eye of the brain that controls thoughts and actions. Its main job is to control the emotional responses to stress by regulating the amygdala.
Social Buffering: ↑ The process that happens when social support helps the brain regulate the stress response. Maternal buffering is social buffering that comes specifically from our mothers or other shut caregivers.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of whatsoever commercial or financial relationships that could exist construed equally a potential conflict of interest.
References
[1] ↑ Hostinar, C. E., Sullivan, R. M., and Gunnar, Yard. R. 2014. Psychobiological mechanisms underlying the social buffering of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical axis: a review of beast models and human studies beyond development. Psychol. Bull. 140(1):256–82. doi:10.1037/a0032671
[2] ↑ Gee, D. Grand., Gabard-Durnam, 50., Telzer, E. H., Humphreys, Grand. 50., Goff, B., Shapiro, M., et al. 2014. Maternal buffering of human being amygdala-prefrontal circuitry during childhood but not during boyhood. Psychol. Sci. 25:2067–78. doi:10.1177/0956797614550878
[3] ↑ Guassi Moreira, J. F., and Telzer, E. H. 2016. Mother withal knows best: maternal influence uniquely modulated adolescent reward sensitivity during risk taking. Dev. Sci. i–11. doi:10.1111/desc.12484
[4] ↑ Gee, D. G., Gabard-Durnam, Fifty. J., Flannery, J., Goff, B., Humphreys, Grand. 50., Telzer, E. H., et al. 2013. Early developmental emergence of human amygdala–prefrontal connectivity after maternal deprivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.South.A. 110(39):15638–43. doi:10.1073/pnas.1307893110
Source: https://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frym.2017.00071
Posted by: demelobunecand.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Where Is Fear Registered In The Brain?"
Post a Comment